Is there any real difference between 3000mhz and 3200mhz RAM? If you’re searching for a new RAM upgrade for your PC, you might be wondering which RAM chip will give you a better performance.

Ultimately, the difference between a 3000mhz and 3200mhz RAM chip will not be very noticeable. Even for those with a keen eye, it will be difficult to tell the difference because both are quite high clock speeds and offer a high level of performance. The only notable time you’ll be able to tell the difference is during benchmark tests. Therefore, during everyday usage, you’re unlikely to see the difference.
When speaking strictly about clock times, 3200mhz is faster and slightly better than 3000mhz. However, when talking about RAM, you also need to consider other factors such as latency to see the whole picture of the RAM chip you’ll be purchasing. In this guide, we’ve assembled everything you need to know about RAM timings and performance before deciding for your PC.
| Key Specifications | |
| 3000mhz |
|
| 3200mhz |
|
Contents
Difference Between 3000 and 3200 RAM
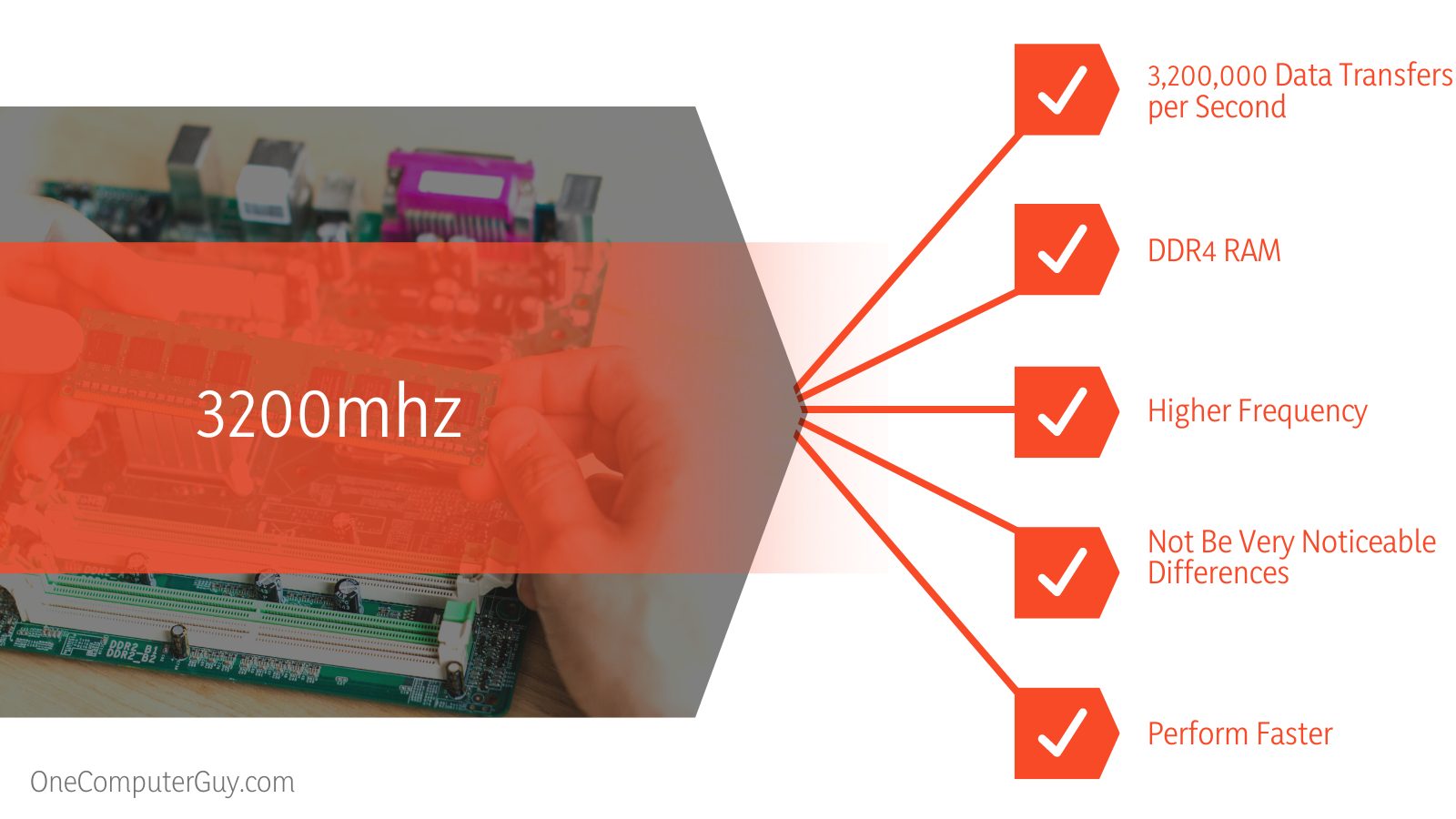
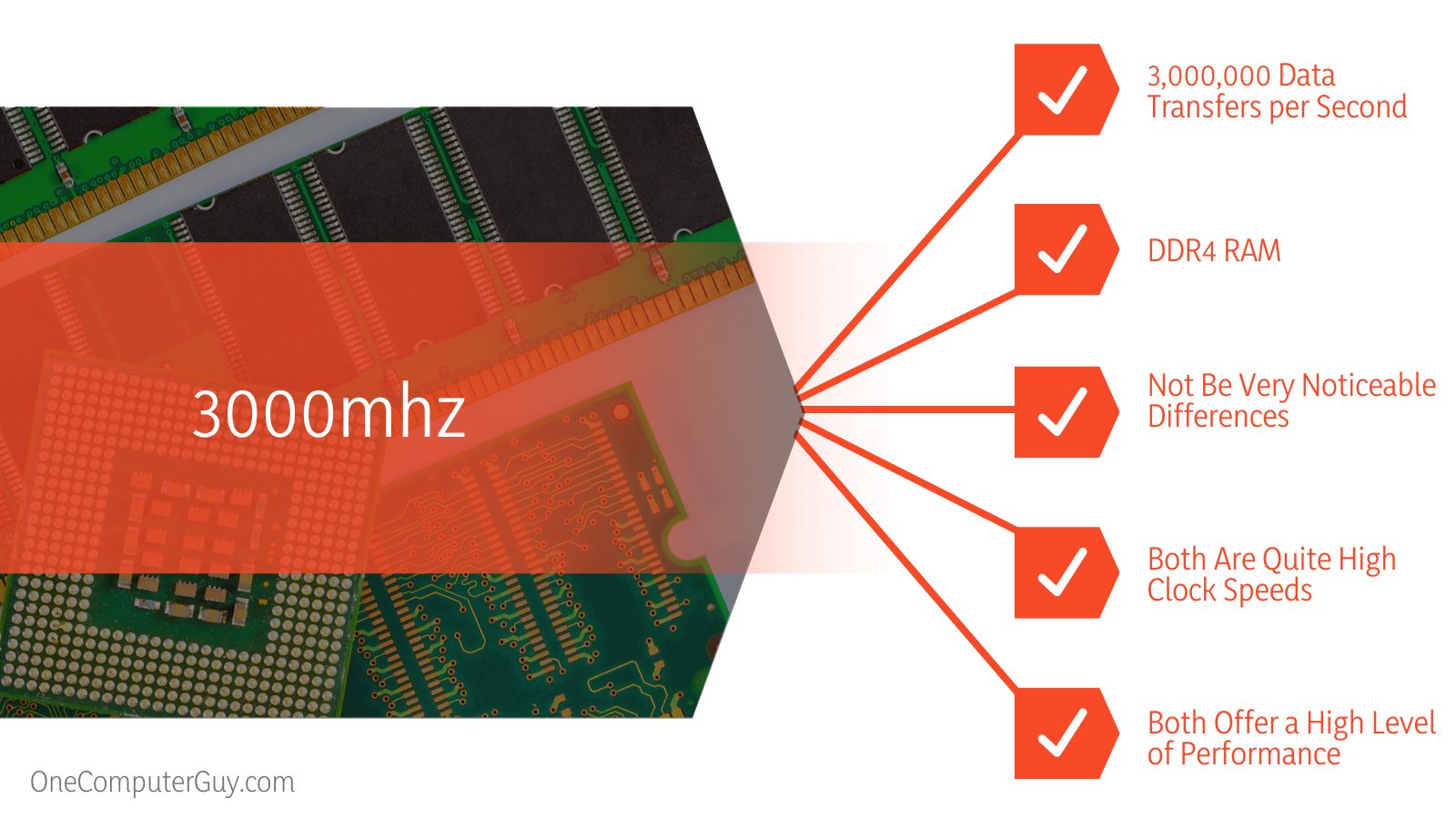
The main difference between 3000mhz and 3200mhz is, 3200mhz is faster and slightly better in terms of clock times and can transfer roughly 6.6% more data per second than 3000mhz.
3000mhz and 3200mhz are both measurements of the speed or frequency of RAM, which is the number of cycles or operations per second you RAM do. What does this mean? RAM speed is measured in megahertz (MHz), which is a measurement of how many mega transfers your RAM can complete in one second. One mega transfer is equal to 1,000,000 data transfers.
This means that 3000mhz RAM can complete 3,000,000 data transfers per second, while a RAM chip with 3200hmz can complete 3,200,000 data transfers per second. This means that 3200mhz RAM can transfer roughly 6.6% more data per second than 3000mhz RAM.
RAM speeds have radically increased through time. DDR2, which was used not so long ago, had speeds of 400mhz to 1066mhz. Today, with DDR4, speeds of 2133mhz even up to 4266mhz are considered normal. The higher the RAM speed, the shorter the duration of one cycle and therefore the more it can process in less time. This is why higher RAM speeds/frequencies are preferable.
Ultimately, the higher the frequency of RAM, the better. Therefore, 3200mhz RAM will generally be better than 3000mhz RAM, offering a slight improvement. However, frequency is not the only consideration. You also need to consider the latency, which we will explain later on.
It is necessary to mention that while some may insist that it’s necessary to have the absolute highest RAM frequency, this is not very accurate. Once in the higher range of frequencies, increasing your MHz further won’t offer much of a performance boost. Why is that the case?
At a certain point, your CPU stops being able to keep up! So, RAM frequency matters as long as your CPU can keep processing all of the data RAM are sending it. However, once you start reaching up into high frequencies like 4266mhz, your CPU simply is unable to process all of the data RAM is sending it, rendering the “improvement” of your higher frequency RAM irrelevant.
What is DDR4?
Both 3000mhz and 3200mhz RAM are classified as DDR4 RAM. What is DDR4 RAM and what difference does it make when comparing it to DDR3 or DDR2?
DDR4 SDRAM stands for “double data rate 4th generation synchronous dynamic random-access memory”. DDR4 is currently the latest operational generation for computing memory. DDR5 was released in 2020 but is not currently widely used. Therefore, DDR4 is still at this point is still the industry standard for gaming.
DDR4 RAM was released to the consumer market in 2014 and was the successor to DDR3 RAM. Compared to the transfer rates supported by DDR3 RAM, DDR4 was a big improvement; DDR3 RAM supported 800mhz to 2133mhz, while DDR4’s lowest supported rate is 2133mhz and it goes up to a whopping 4266mhz. That’s 4266 million transfers per second!
With DDR4 RAM came not only these greatly increased clock speeds, but also reduced latency and lower power consumption. The decreased power computation is an important innovation. DDR4 RAM runs efficiently at 1.2v whereas DDR3 RAM requires at least 1.5v and up to 1.97v to run efficiently.
Why is decreased power consumption important? Most notably, it allows higher transfer rates at lower voltages which leads to increased system stability. This reduces the risk of overclocking causing damage to your machine and overall reduces the strain that intensive programs and games put on your PC.
Are there any differences between different transfer rates among DDR4 RAM modules? Since DDR4 RAM supports transfer rates from 2133mhz to 4266mhz, there is quite a range in DDR4 RAM chips. A DDR4 RAM chip with 4266mhz will achieve 4266 million transfers per second, double that of what a 2133mhz RAM chip can do.
Because you’re deciding between 3000mhz and 3200mhz, you’re therefore deciding between two DDR4 RAM cards. Both speeds benefit from DDR4’s decreased power consumption and increased system stability. Ultimately, any DDR4 chip will serve you well for gaming unless you’re looking to operate on maximum power-settings or be on the cutting edge of gaming. If you are on the cutting edge of gaming, it might be better to save you money for when DDR5 is released to the public!
Ram Frequency vs Latency?
RAM frequency or speed is not the only factor to take into consideration when updating your RAM. What you also need to consider is the latency of the RAM. Column Access Strobe (CAS) latency is the main type of latency to consider and will appear in the specs of all RAM cards as “CL_” or “C_” with a number in the blank space. What exactly is latency?
Latency refers to timing. While frequency measures the number of data transfers per second, the latency refers to the amount of delay in between the call to transfer data and when that transfer is executed. Therefore, the CAS latency of RAM describes the specific amount of time it takes between the RAM being told to access a particular data set in one of its columns by a memory controller and when it makes that data available.
In other words, CAS latency refers to the number of clock cycles between the moment when the CPU sends a request to the RAM and the moment when the RAM performs the operation.
As an example, let’s take two examples of CAS latency and compare them. If one RAM chip has C14 and the other C16, which one is faster? C16 RAM will have a total of 16 clock cycles in between when the CPU requests data from the RAM and when the RAM performs the operation. On the other hand, C14 RAM will have only 14 cycles between these two processes. That means that C14 is faster than C16.
Thus, the general rule is that the lower the CAS latency, the better and faster your RAM performs.
So you might be wondering how this information relates to RAM frequency. Ultimately, both RAM latency and frequency are responsible for the overall performance of your RAM, because both latency and frequency are connected to the clock cycle. While RAM frequency determines how long a clock cycle is, the CAS latency determines the delay in the number of clock cycles that occur between when the RAM receives a request and when it performs it.
Let’s see some examples of what this means.
If you compare two RAM chips with the same frequency, it is necessary to check out which RAM chip has the lowest CAS latency. While both RAM chips might be 3200mhz, they can have different performances if one has a CAS latency of 14 and another has a CAS latency of 16, with the C14 performing better and faster than the C16 despite having the same frequency.
This also goes for two RAM modules with the same CAS latency and different frequencies; the RAM chip with the higher frequency will be preferable. For example, if you are comparing two RAM chips that have C15, one with 3000mhz and the other with 3200mhz, the 3200mhz will perform faster because of its higher frequency.
The Verdict: 3000mhz vs 3200mhz
At this point, you’ll understand that the answer to picking 3000mhz or 3200mhz RAM is not as simple as you maybe thought. This is because you have to not only consider the frequency, but also the latency of the RAM. If all of this information has confused you even more, worry not!
The best practice for choosing RAM is to pick the RAM within your budget that features:
1. The highest frequency available and
2. The lowest CAS latency available.
Following these two rules will ensure that you will achieve the highest performance possible within your budget. This is because you’ll be both maximizing the amount of data your RAM can send per second while also minimizing the delay between operations.
If you’re trying to decide between RAM chips with the same latency and one is 3000mhz and 32000mhz, then your job is easy; the best choice will be the RAM with 3200mhz.
However, if you’re trying to decide between two different RAM chips with different speeds/frequencies and different latencies, there is a mathematical formula you can fill out to see which one will perform faster.
The formula simply divides the RAM speed by its latency. This will give you a “value” (not indicative of speed, just a number for comparison); the higher the number you get for “value”, the better.
The formula is below:
Speed / CAS latency = value
Below is an example comparison of two different RAM chips using the formula. One RAM chip has a frequency of 3000mhz with a latency of C15, and another RAM chip has a frequency of 3200 and a latency of C16. Which one is better?
3000 (speed in MHz) / 15 (CAS latency) = 200
3200 (speed in MHz) / 16 (CAS latency) = 200
In this case, the performance of these two RAM chips is identical! Although one has a higher speed, its higher latency alters the performance to be equal to the level of a RAM chip with lower speed but higher frequency.
This serves as a demonstration of how frequency and latency work hand-in-hand to produce the total overall performance of a RAM chip. Use this formula if you’re ever stuck between two different models and want to figure out which one is better.
Final Thoughts
In summary, while a RAM chip with a high frequency is certainly preferable to one with a low frequency, both 3000mhz and 3200mhz are relatively high frequencies. This means that either RAM chip will guarantee a high level of performance for your PC. Ultimately, it will be difficult to tell the difference between the two frequencies.
If you want the better of the two, got for a RAM chip with 3200mhz and the absolute lowest latency possible. This will offer you slightly better performance than a RAM chip with 3000mhz and a higher latency.







Thank you for this article! Very helpful