Knowing the differences between WAN vs LAN can help you make the right decision when choosing a network for your home or business. Our networking experts have provided us with some insights which we’ll be sharing with you.
 At the end of this article, you’ll be able to understand the differences between LAN versus WAN as well as when and where to use them.
At the end of this article, you’ll be able to understand the differences between LAN versus WAN as well as when and where to use them.
Contents
- Let’s Start With Some Networking Basics: What Is a Network?
- What Is a Local Area Network?
- What Is a Wide Area Network?
- The Difference Between Local Area Network and Wide Area Network
- What Is LAN Useful For?
- What Is a WAN Useful For?
- Pros of Using a LAN
- Cons of Using a LAN
- Pros of Using a WAN
- Cons of Using a WAN
- Routers, LAN, and WAN: What’s the Connection?
- The Role of a Router
- Conclusion
Let’s Start With Some Networking Basics: What Is a Network?
A network is a group of interconnected devices, computers, and peripherals with the ability to communicate with each other.
There are mainly two types of networks: local area network and wide area network.
What Is a Local Area Network?
A local area network, otherwise known as LAN, is a network in the same geographic area or a limited area. Examples of places where you can find a LAN network include schools, office buildings, laboratories, and homes.
Local area networks are excellent for sharing resources such as printers, files, and games, and they are often limited to a single building. A LAN can consist of laptops, PCs, tablets, smartphones, TVs, and more.
Wired LANs are connected via cables and can transmit data throughout the entire limited area. Wireless LANs, on the other hand, are limited to the range of an access point, such as a wireless router. You can extend their range by adding multiple access points to the network.
What Is a Wide Area Network?
Unlike LANs, wide area networks span across a wide geographical area. A WAN can cover anywhere from an organization or enterprise to a state, country, or even the entire world. You can consider the Internet itself as a type of WAN.
A wide area network can also be a connection of LANs connected through radio waves or telephone lines to span across a wide geographic location. Wide area networks connect local area networks to one another, unlike LANs that connect devices and peripherals to each other.
Note that WANs in a city, such as the ones used in a group of offices belonging to an organization, are known as metropolitan area networks.
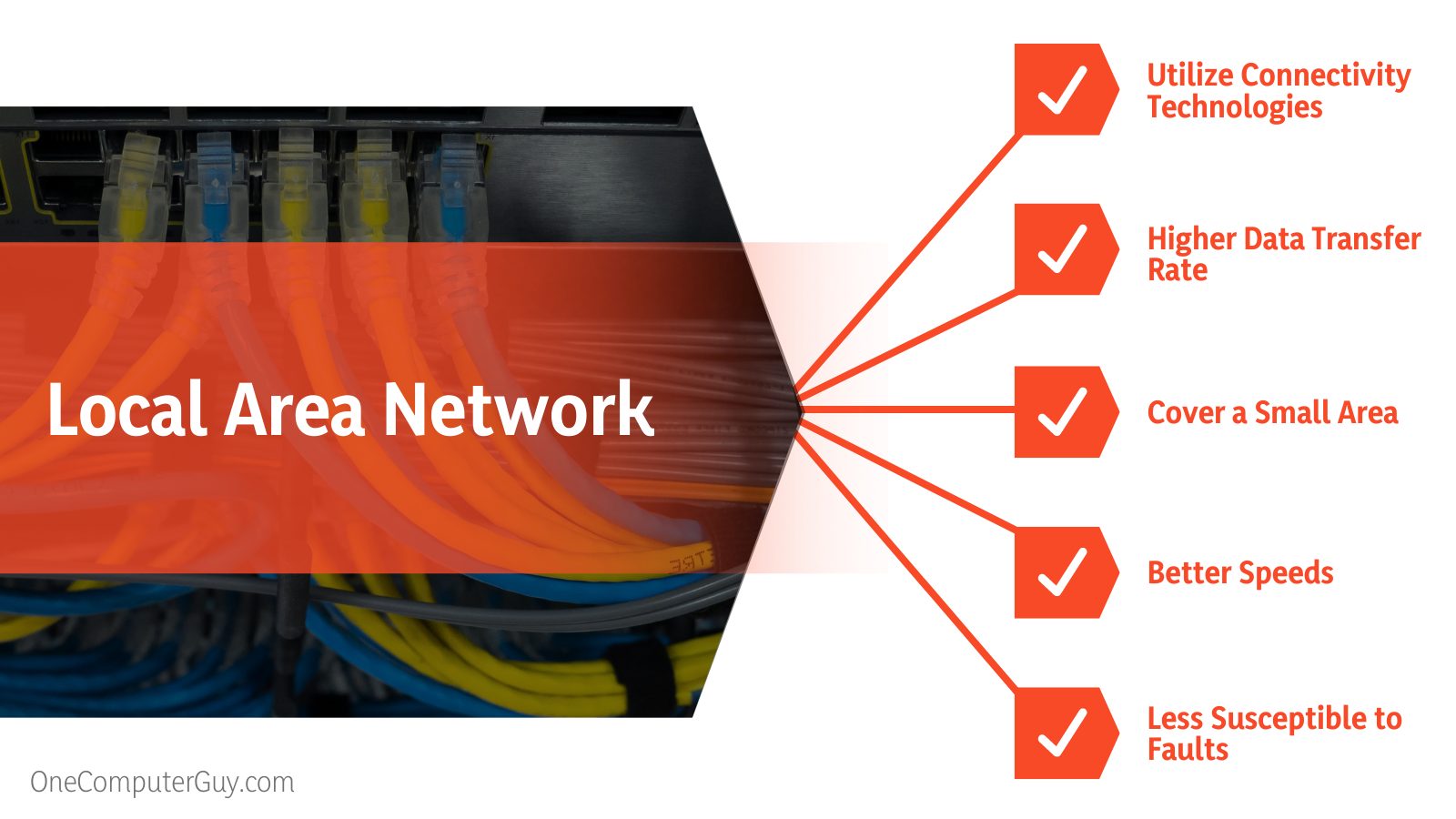
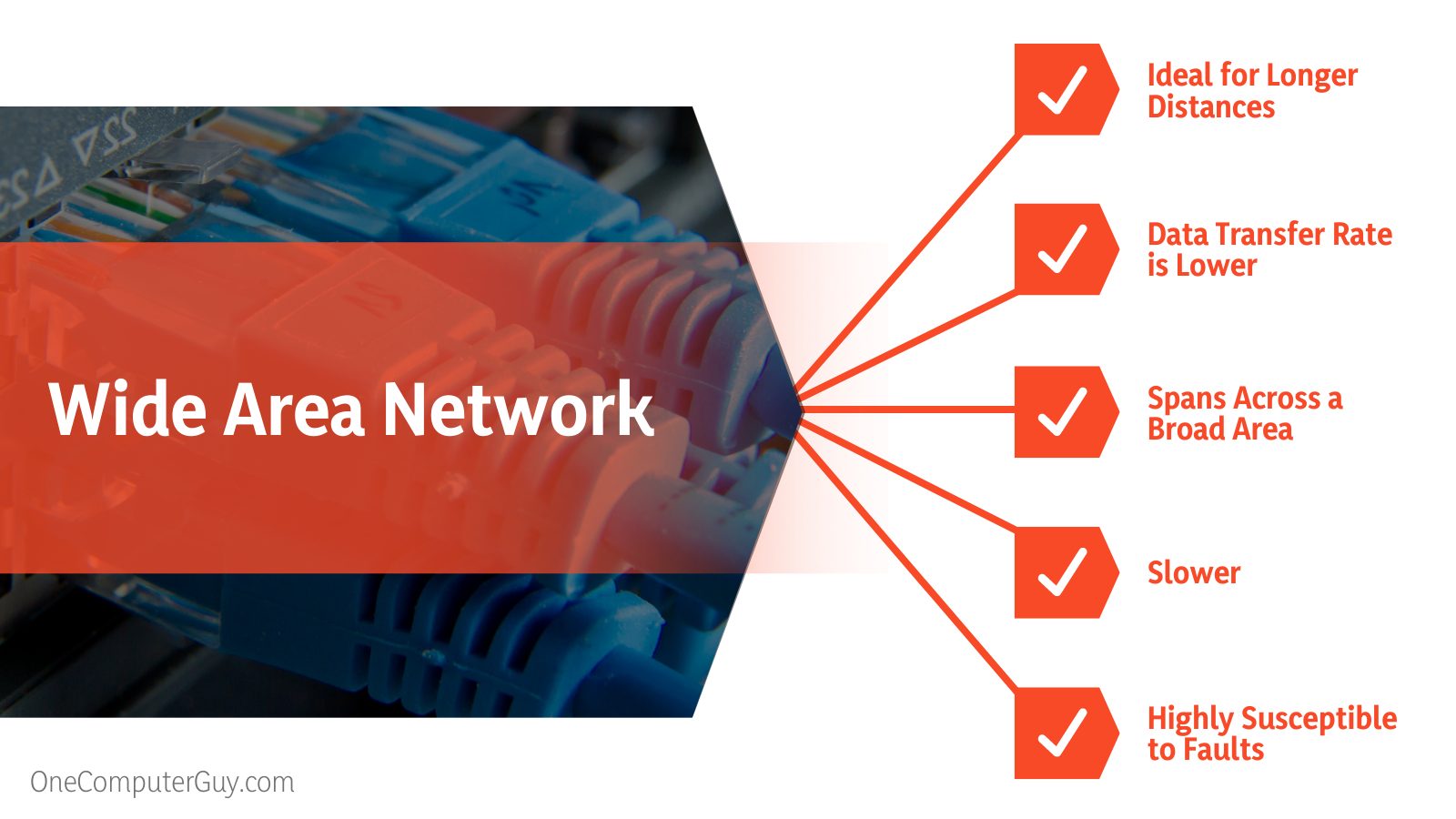
The Difference Between Local Area Network and Wide Area Network
| Local Area Network | Wide Area Network |
| Local area networks utilize connectivity technologies like token and ethernet. | Ideal for longer distances, such as X.25 and Frame Relay. |
| LAN offers a higher data transfer rate. | A WAN’s data transfer rate is lower. |
| Local area networks cover a small area. | A wide area network is a computer network that spans across a broad area, such as cross-regional and metropolitan boundaries. |
| LAN offers better speeds. | The speed of a WAN is slower. |
| LAN is less susceptible to faults. | WAN is highly susceptible to faults. |
| The downtime incurred when a LAN is faulty is low. | The downtime for a faulty WAN is high. |
| The design and maintenance of a local area network is relatively easy. | The maintenance and design is sophisticated and may require the help of experts. |
| Offers short propagation delay time. | Offers a longer propagation delay time. |
What Is LAN Useful For?
Local area networks are ideal for many different use cases. As we noted above, LANs help you share resources like scanners and printers.
They are also excellent for software developers who want to share their development and testing tools within an office.
– It Can Be Used as a Server
A computer in a local area network can be used as a server, allowing you to monitor and manage other devices and computers in your network.
You’ll also have the capability to store different software on the server. This software can be made accessible to all computers on the network instead of buying the software for each computer.
– It Can Be Used to Enhance Team Communication
Local area networks are ideal for improving team communication and efficiency without the need to connect to the internet. A LAN connects the workstations in the building to each other, allowing them to communicate easily and making it easy for users to send data to each device in the network.
What Is a WAN Useful For?
Wide area networks are more sophisticated than local area networks. They are used for complicated businesses and processes.
Some good use cases include:
- A highly secured network utilized for military operations
- Airlines and railway reservations use wide area networks
- Corporate offices looking to share data with their regional offices can do so by using a centralized node
WANs are used in universities allowing people like the dean and lecturers to share resources and information. A wide area network also makes it easy for workstations to be connected locally, thereby allowing each node to communicate with each other without an internet connection.
Resources like scanners, printers, fax machines, and even hard disks can be used to share the nodes publicly.
Pros of Using a LAN
- LANs allow you to use the same software over the network instead of buying new software for each computer in the network
- Using a local area network minimizes the need to purchase multiple hardware as resources like DVD-ROM, hard disks, scanners, and printers can be used by each client on the network
- A LAN allows you to send messages and data to different computers in the network without an internet connection
- Your data gets more secure as you’ll be able to easily manage your data from a single server
- The data of all users on your network can be stored on the hard disk of your server computer
- LAN users on your local area network can share a single internet connection, thereby reducing hardware and installation costs
Cons of Using a LAN
- While the security might be good, LANs do not offer excellent privacy because the LAN admin has the ability to check the personal data files of each client in the network
- Local area networks need constant administration because they are susceptible to hardware and software failures
- If the LAN admin is unable to secure your data repository, unauthorized users can gain access to critical company data
- The initial installation cost of a LAN is quite high even though you’ll save cost over time
Pros of Using a WAN
- WANs allow businesses situated at longer distances to communicate effectively as they cover a wider geographical area compared to LANs
- Wide area networks can include multiple devices, including gaming consoles, mobile phones, laptops, tablets, and computers
- A WAN allows you to share files and data over a larger area
- They share resources and software via multiple workstations
- Wide area network connections utilize the radio transmitters and receivers their client devices are designed with
Cons of Using a WAN
- The initial cost of setting up a WAN is expensive than the setup cost of a LAN
- Maintaining a WAN by yourself is difficult
- You’ll need to hire proficient network administrators and technicians to help you monitor your WAN
- Resolving technical issues takes more time as there are various wireless and wired technologies involved in making a wireless area network
- WAN security is subpar when compared to the security offered by other network types
Routers, LAN, and WAN: What’s the Connection?
Most wireless routers are designed with at least one LAN port and one WAN port. In most small businesses and homes, the WAN port on a router is connected to a high-speed modem, such as a cable or DSL modem which connects the router to the internet. You’ll be able to identify this port by the “internet” or “WAN” tag the manufacturer places on it.
On the other hand, the LAN port is connected to computers with no internet access via an Ethernet cable. This connection provides the computer with access to the internet as well as access to other computers on the network, just like when you use Wi-Fi.
Although routers are built to connect to wireless devices, such as computers, tablets, and laptops wireless, many of them come with physical ports that allow you to connect your devices directly. Unlike Wi-Fi, wired LAN connections, like an Ethernet or USB connection, are less prone to interference.
The omission of interference makes them faster than Wi-Fi. For instance, most Wi-Fi routers offer up to 800 megabits per second, or 800mbps, when transmitting over Wi-Fi. But when you use an Ethernet connection, you can get up to three GigaBytes per second, or 3Gbps, depending on the router’s capability and your internet speed.
However, for routers to offer internet capabilities, they need to be connected to the public internet. This connection is often done with an Ethernet cable that will connect your router to a modem provided by your internet service.
In some cases, your router can also double as a modem, in which case the router is connected via a phone jack or a cable line instead of an Ethernet cable.
Simply put, the port labeled LAN on your router is used to connect computers to your network. You can connect multiple computers to your network—if your router has multiple ports—and share files between these computers without using the internet.
The port labeled WAN, on the other hand, is used to connect your router to the outside world, which in most cases, is the internet.
The Role of a Router
Wireless routers are designed to provide two main roles: data protection and internet sharing. To receive data, files, or information from the internet, your internet-enabled device needs an internet protocol address, otherwise known as an IP address.
An IP address helps other computers identify where to send data to. Your router serves as the gatekeeper between the internet and the devices in your local area network. It has its IP address as well as the capability to assign IP addresses to each device on the network.
Computers outside your network are unable to identify the IP addresses assigned by your router. This process makes your devices secure as hackers and exploiters will find it difficult to gain access to the devices in your local network. Some routers even come with advanced features such as encryptions and firewalls to add even more security to your network.
Conclusion
We’ve covered a lot of ground on the difference between a LAN and a WAN. Here are some points to keep in mind when deciding on the ideal network for your home or business.
- LAN is a private network while WAN can be public or private
- Local area networks offer more speed when compared to wide area networks
- LAN experiences lower congestion than WAN
- Local area networks offer more fault tolerance than wide area networks
- WAN covers a large geographical area while LAN covers a small area
- Maintaining and designing a WAN is complicated and may require technical expertise
- Designing and maintaining a LAN is easy and less complicated
- LAN uses cables such as co-axial, Ethernet, and UTP cables as its communication and transmission medium
- WAN uses radio waves, satellite links, or PSTN as its transmission and communication medium
With our discussion above, choosing the ideal network between WAN vs LAN shouldn’t be a difficult process for you. If you’re looking to create a network setup for your home, a small business in a building, or your game room, a LAN is the perfect network type to choose. But if you have multiple locations across different geographic areas or have many remote users spread around the country, choosing a WAN is the way to go.







