What are the differences between quad core vs 6 core? Is it true that the more cores you have, the better and faster your computer will be?
 We asked computer technicians and enthusiasts to help us understand the differences between both. In this article, we’ll be passing their knowledge and insights to you.
We asked computer technicians and enthusiasts to help us understand the differences between both. In this article, we’ll be passing their knowledge and insights to you.
| Product | Key Specifications |
| Quad Core |
|
| 6 Core |
|
Contents
What Are the Differences Between 4 Core vs 6 Core?
There are many differences between 4-core vs 6-core processors, including speed, number of cores, power consumption, and more. We’ll help you understand the differences and answer some of the most frequently asked questions about quad-core vs 6-core processors.
– Cores
The main difference between quad-core vs 6-core processors is the number of cores they have. Hexa-core CPUs, otherwise known as 6-core CPUs are designed with six cores while quad-core CPUs have 4 cores. But do more cores give you an edge?
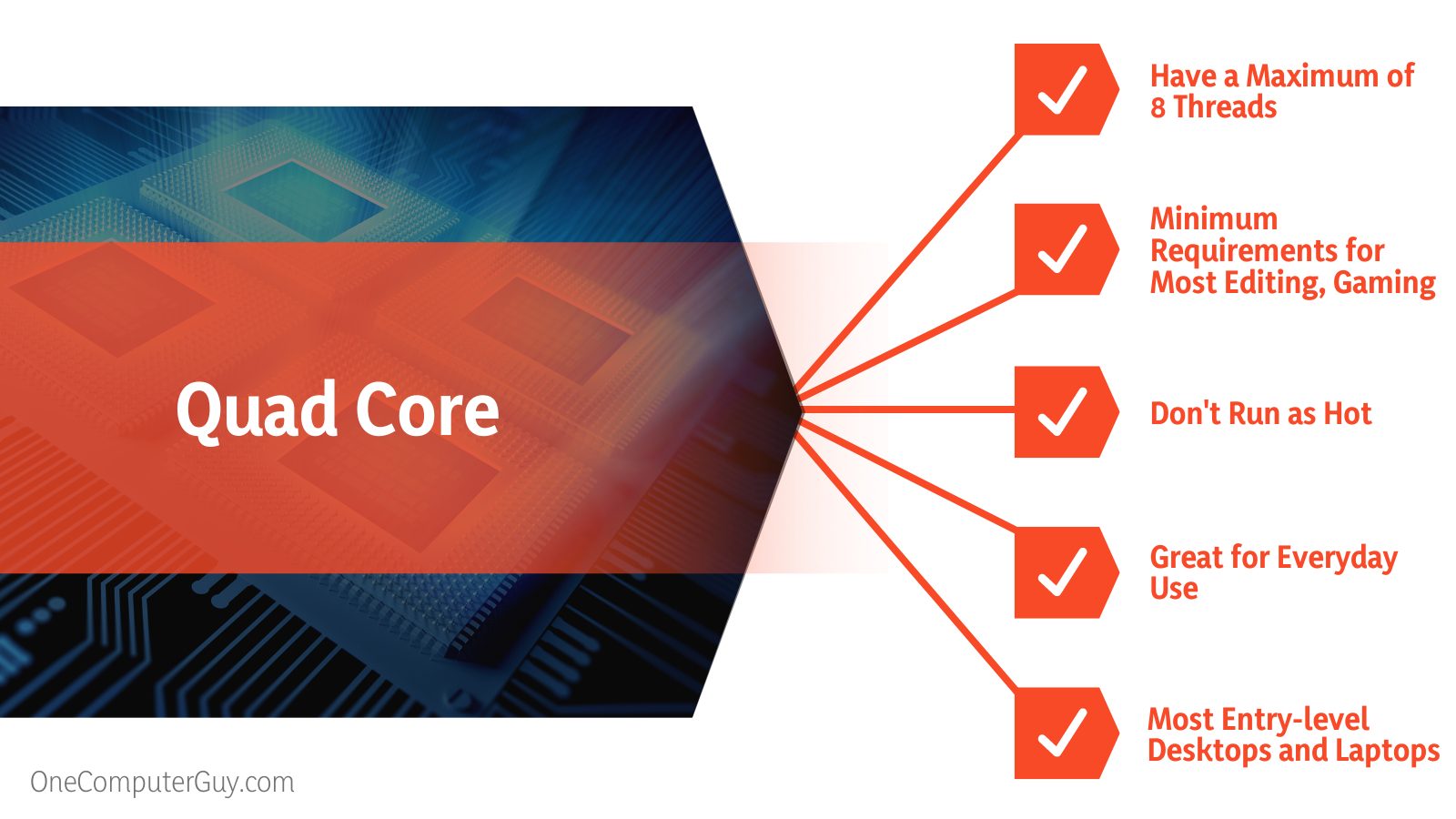
Yes, they do. Four cores in a CPU are the minimum requirements for most editing, gaming, and graphics software. Although the programs will run, the cores won’t allow you to enjoy the maximum functionality or speed of these programs.
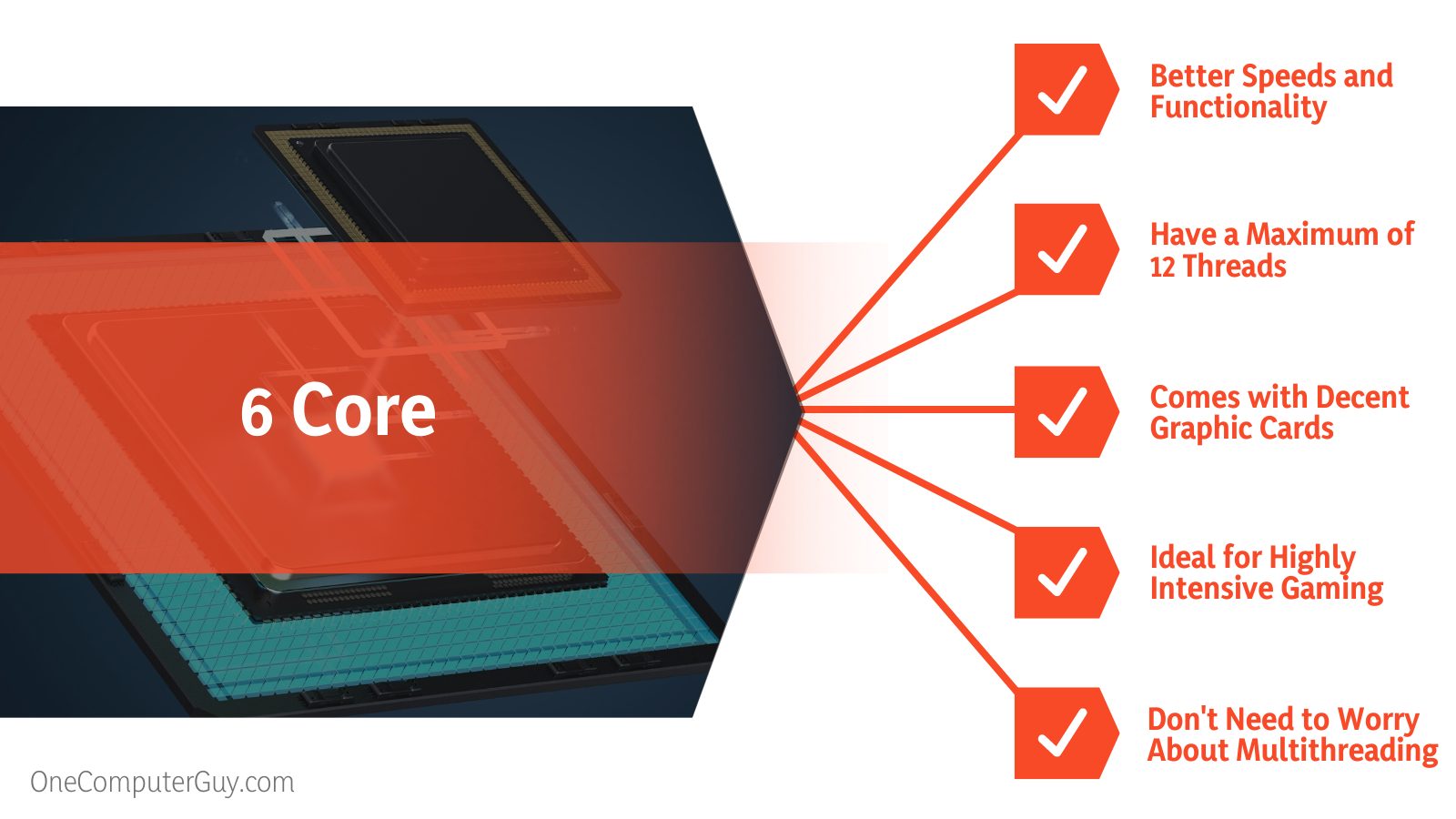
A six core processor, on the other hand, will provide you with better speeds and functionality. You’ll be able to load software faster and play games at better frame rates.
The difference in threading is another reason why six-core processors have an edge over quad-core processors. Hexa-core processors can have a maximum of 12 threads while 4-core processors can’t have more than 8 cores. The higher the number of threads on a CPU, the better its strength and capability to perform heavy tasks.
– Processing Speeds
The processing speed or clock speed of a CPU refers to how fast a CPU can finish its task. It indicates the number of times a processor can perform tasks per second. For instance, if your CPU has a clock speed of 5GHz, it means that the CPU can perform up to 5 billion cycles in one second.
– Understanding Base Clock vs Boost or Max Clock
You’ll notice that most CPUs are advertised as having base clocks and max clocks. This is because CPUs are designed to conserve power when you’re not doing intensive tasks, and unleash power when the task is high.
The base clock of a CPU is the power and speed your computer provides when it’s idle or performing low-intensity tasks. So if you have an expensive CPU and you’re using Microsoft Word or streaming movies on Netflix, your CPU won’t be doing a lot.
Max clock, on the other hand, is the speed and power provided by your CPU when you’re carrying out intensive tasks, such as gaming at high frame rates or rendering 4K videos.
Higher base clock and boost clocks are always better. However, it depends on whether the task you’ll be performing will make use of the cores in your CPU or not. For instance, if you have a quad-core CPU and the task you’re running requires just two cores, your quad-core CPU will provide sufficient speed. But if the task you’re performing takes up all four cores, having a 6-core processor will be better in this scenario.
So basically, the higher the intensity of the task you want to perform, the higher the number of cores your CPU should have.
 – Threads
– Threads
Computer chip manufacturers, such as Intel and Ryzen, utilize multithreading to provide a core with virtual cores or threads. These threads allow your CPU’s cores to divide certain tasks between each other.
For instance, when a thread is waiting for you to enter some data to complete a task, a second thread can start doing the prep work for saving the task.
While the real-world gains from thread counts are minimal, having more isn’t a bad idea. Most modern CPUs, whether quad-core or 6-core, have at least 2 threads per core. So there’s no need to pay too much attention to threading when considering CPU cores.
– IPC
Instructions per cycle or clock (IPC) plays an important role in the speed of a CPU. It represents the number of instructions or tasks a CPU can complete in one cycle. This spec is an important one because even if your CPU has a high clock speed, but low IPC, it will be slower than a CPU with low clock speeds but high IPC.
IPC is often measured in review benchmarks. You won’t find them on product listings as they’re not advertised. The general rule to follow here is the more recent the Intel or AMD chip, the better their IPC will be.
– Thermal Design Profile
Thermal Design Profile (TDP) refers to the amount of power needed by your CPU. It’s measured in watts and can affect your electricity bill. Many CPU manufacturers offer a single TDP figure, e.g. 65 watts. Single TDP figures are usually the max wattage required by your computer’s CPU when it’s under heavy loads.
However, there are CPUs that come with maximum and idle or base TDPs. The idle TDP refers to the amount of power needed by your CPU when it’s calmer. TDP doesn’t affect your CPU’s performance, but it can contribute to the amount you pay on electricity bills. The more powerful the processor, the higher the TDP.
TDP is also an important factor for figuring out the kind of CPU cooling you’ll need for your rig. A typical quad-core CPU will have a lower TDP when compared to a 6-core CPU. Also, the amount of power your 6-core or quad-core computing chip will consume will depend on its architecture.
For instance, a standard quad-core Core i5 7th generation processor from Intel has a TDP of 91 watts while the low power models like the Core i5 7400T only take about 35W of power. The cheapest AMD Ryzen 3 quad-core processors consume between 12-25 watts of power while the high-end models eat up to 35 to 65 watts of power.
An Intel 6-core processor like the Coffee Lake-S eighth and ninth generation models has a TDP between 65 watts to 95 watts. The latest Comet Lake-S processor consumes up to 125 watts of power. Low-end 6-core CPUs from Intel tend to consume up to 35 watts of power while those from AMD consume about 15 to 54 watts maximum. AMD’s high-end chips consume as much power as their Intel counterparts with TDPs ranging from 65 watts to 95 watts.
– Heat Generation
The rate at which your PC generates heat is an important factor to consider whether you’re building from scratch or buying one. The higher the number of cores working in your PC, the more heat it will generate. However, with enough cooling and airflow, this shouldn’t be a problem.
The new generation of AMD and Intel chips pay special attention to heat generation. Modern processors are intelligently built to turn off their non-working cores or keep them at low power so your PC won’t generate much heat. While practical usage affects how hot a PC runs, a typical 6-core processor will run hotter than a quad-core processor when all cores are working.
– Integrated Graphics
Integrated graphics are often decided by the PC brand. Having an integrated graphics card means that you won’t need to purchase an external graphics card, except it’s necessary.
Quad core processors have a good chance of having integrated graphics cards. These graphics cards may not be very powerful but they can offer decent functionalities.
Six-core processors on the other hand tend to come with decent graphic cards. However, the cards they come with cannot provide the functionalities, speed, and display you’ll get from external GPUs.
4 or 6 Core for Gaming: Which Is Better?
You’re thinking 6-core processors should be better than quad-core processors, right? While this isn’t far from the truth, there are still exceptions.
 – Multithreading Quad-Core Processors
– Multithreading Quad-Core Processors
Quad-core processors are great for everyday use and you’re going to find them in most entry-level desktops and laptops. However, that doesn’t rule out their ability to handle gaming. If you’re a casual gamer who’s looking for decent performance at a cheap price, going with a quad-core PC will be in your best interest.
Be on the lookout for quad-core processors with eight threads. Unlike their four-thread counterparts, eight-thread quad-core processors offer multithreading capabilities.
They are more expensive than their four-thread counterparts, but they offer better performance and can serve as the sweet spot between price and performance. You can also use them for home theater PCs.
– 6-Core Processors for Gaming
Six-core processors are ideal for highly intensive gaming. Their cores are designed to handle most workloads in today’s environment. Whether you’re an MMO gamer, video producer, or full-stack application developer, a six-core CPU will provide you with optimal performance.
Six-core processors are also available with and without multithreading functionality. So, if you run apps that support multithreading and are looking to get a 6-core processor, ensure that your processor comes with multithreading.
Most games won’t use multithreading on a six-core CPU. So if you’re getting this processor for gaming, you don’t need to worry about multithreading.
Which CPU Spec Is the Most Important?
The specs we’ve talked about above are the main parts you need to worry about. However, clock speed, IPC, and the number of cores in a CPU are the most important determinants.
 For those who aren’t tech-savvy or can’t figure out what to look for, a general rule of the thumb you can follow is that the more recent the chip generation, the better it’s going to be.
For those who aren’t tech-savvy or can’t figure out what to look for, a general rule of the thumb you can follow is that the more recent the chip generation, the better it’s going to be.
This rule implies that the latest AMD and Intel chips will offer the best clock speed, IPC, and cores at their respective price range and level. So a 10th gen quad-core processor is bound to be better than a 6th-gen quad-core processor.
Conclusion
We hope you’ve been able to learn the difference between quad-core vs 6-core processors. Here is a quick summary to help refresh everything you’ve read.
- Quad-core processors have four cores while 6-core processors have 6 cores.
- Six-core processors offer more functionality than quad-core processors.
- The base clock of a CPU is the minimum speed at which it operates.
- Boost clock or max clock is the maximum speed your CPU can offer for intensive tasks.
- Hexa-core processors have more threads than quad-core processors.
- Most modern processors come with two threads per core.
- Six-core processors consume more power than quad-core processors.
- Quad-core processors generate less heat than 6-core processors.
- Most modern CPUs are designed with integrated graphics cards.
- Integrated graphics cards are not as good as external GPUs.
- Quad-core processors are great for casual gaming with normal graphics.
- Six-core CPUs are ideal for intensive gaming.
Modern generation computers are moving from quad-core CPUs to 6-core CPUs thanks to their longevity and functionalities. However, while having more cores is always a good thing, you need to ensure that the task you want to perform will be using all cores. If you’re not performing any intensive task, a computer with a quad-core CPU is a good buy.