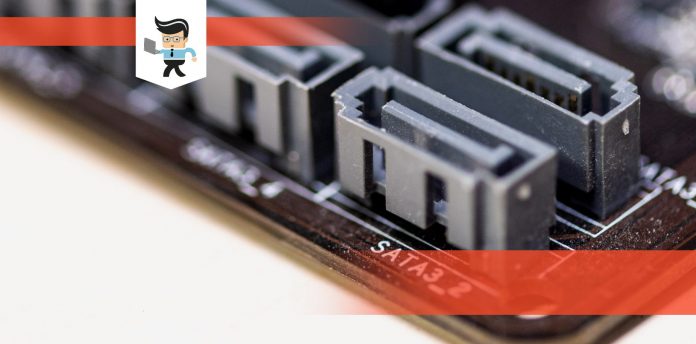
You can add more SATA ports to your computer via a SATA expansion card. SATA ports allow you to connect your SSDs, HDDs, and optical drives to your computer’s motherboard.
 A SATA expansion card is connected via PCIe and can be designed with more than one connector to connect your storage devices to your computer. In this article, we’ll be sharing insights from our computer experts on how to get more SATA ports added to your computer.
A SATA expansion card is connected via PCIe and can be designed with more than one connector to connect your storage devices to your computer. In this article, we’ll be sharing insights from our computer experts on how to get more SATA ports added to your computer.
Contents
Why You May Need More SATA Ports
SATA ports are mainly for adding more storage drives to your computer. Most motherboards come with two to six SATA ports.
If you’re building a normal PC you want to use at home, two SATA ports should be enough. But if your build is like a NAS PC that requires multiple storage devices, then you’ll need extra SATA ports depending on your storage needs.
How To Add More SATA Ports
As we noted earlier, adding more SATA ports to your computer requires you to have a SATA expansion card. However, there are a wide variety of SATA expansion cards to choose from.
Some are small while others are large. Some are designed with RAID controllers while others don’t have them. Some are cheap and can be used for normal home builds, while others are expensive and ideal for professionals.
It all depends on your preference and wallet. Here are the different methods you can use to add additional SATA ports to your PC:
-
SATA Hub Port Multiplier: For Budget Builds
A SATA hub port multiplier is one of the cheapest ways to add more SATA ports to your computer. This device allows you to turn one SATA port into a host that multiplies your ports. It is inexpensive and one of the common methods to utilize if and when you need more ports for your budget build.
However, as with many cheap things, the SATA hub port multiplier comes with a downside – performance. Since it uses one of the SATA ports on your computer’s motherboard as a host, it means the device will need to get its bandwidth from the host.
What this translates into is low performance as the single SATA port that serves as the host won’t be able to effectively distribute the same amount of bandwidth between the ports attached to it. You’ll be getting a lot of bottlenecks for the drives you connect to your computer via the SATA hub port multiplier.
While they may be inexpensive, they are inefficient and produce low scores on the performance and compatibility board. Unless you’re on a tight budget, we do not recommend that you add SATA ports to motherboard via these expansion cards.
-
SATA PCIe Card: The Normal Standard
The SATA PCIe cards are often the go-to expansion card most people choose when they need more SATA ports added to their motherboard. It’s the general solution for most average users. This SATA expansion card comes in a variety of sizes and each of them comes with a wide range of ports.
 The number of ports on the SATA PCIe card can range from two to eight. However, it’s important that you consider the number of PCIe lanes the expansion card you buy has as doing so will help you understand the downstream and upstream bandwidth of the card.
The number of ports on the SATA PCIe card can range from two to eight. However, it’s important that you consider the number of PCIe lanes the expansion card you buy has as doing so will help you understand the downstream and upstream bandwidth of the card.
It’s important that you understand factors such as PCIe version, throughput rate, and the PCIe lanes of your expansion card before purchasing one. Note that many SATA PCIe expansion cards do not feature RAID controllers. We’ve explained these factors below to help you understand them better.
-
SAS SATA Expansion Card: The King of Them All
The SAS SATA expansion cards are top-of-the-line. They are utilized by professionals and offer excellent downstream and upstream bandwidth. Also, many of them tend to come with a hardware RAID controller. You’re likely to find them being used by professionals and enterprises.
The SAS SATA expansion cards are the ideal method network-attached storage (NAS) users can utilize when adding SATA ports to their computers. These expansion cards are connected via a special cable known as the SAS to SATA cable.
They come with multiple ports so you may need to utilize multiple cables. For instance, a SAS SATA expansion card that can support eight different ports will need two SAS-4 SATA cables to work efficiently.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a SATA Expansion Card
While it’s true that you can get more SATA ports attached to your computer with an expansion card, knowing how these cards work will help you make the right choice for your build. Below are some important factors you need to understand before buying a SATA expansion card.
 – SATA Slot Version
– SATA Slot Version
Before making a purchase, make sure you check out the version of the expansion card you’re buying. The card you choose needs to have the latest port version —version 3.0. Older SATA cards commonly have version 2.0 SATA ports.
The difference in speed between the two versions is huge. While version 2.0 SATA ports offer a maximum transfer speed of three Gbps with a throughput of 375MB/s, version 3.0 SATA ports provide transfer speeds of up to six Gbps with a throughput of 750MB/s.
– Number of Slots the Ports Has
While this may be an obvious factor to consider, it’s still worth mentioning. You want to make sure the SATA expansion card you choose to add extra SATA ports to your computer comes with two to eight different ports.
You should also consider the size as well as the PCIe version of the card to make sure you’ll get a decent amount of bandwidth provided to each slot. Here are more details on why you should consider both factors:
-
Size ad PCIe Version
The PCIe version of your expansion slot also refers to the number of lanes they occupy. Taking the connector size and number of lanes into account will ensure that you get the ideal expansion card for your computer.
SATA expansion cards come with different numbers of connectors, including x8, x4, and even x1. Each of the numbers after the ‘X’ refers to the number of PCIe lanes the expansion card will occupy. This means that an expansion card with an x4 connector will occupy four lanes, an x1 will occupy one, and so on.
 Each of these lanes is designed to offer a specific amount of transfer speed, otherwise known as the throughput rate, depending on the card’s version. For instance, a single-lane version 3.0 expansion card will provide up to 985MB/s while a single lane version 2.0 card offers 500MB/s.
Each of these lanes is designed to offer a specific amount of transfer speed, otherwise known as the throughput rate, depending on the card’s version. For instance, a single-lane version 3.0 expansion card will provide up to 985MB/s while a single lane version 2.0 card offers 500MB/s.
Now, an average hard disk operates at a maximum speed of up to 200MB/s. Let’s assume you have an x1 connector with a PCIe version 2.0 standard and four different ports, the speed you’ll be getting on each port will provide any connected device with serious bottlenecks. For all four ports to provide excellent throughput, the speed provided needs to be at least 800MB/s. But a version 2.0 x1 connector only offers 500MB/s max, which means your hard drive is bound to suffer performance bottlenecks.
-
What if It’s an SSD?
An average solid-state drive has more than twice the speed of an average hard drive. While hard drives provide about 200MB/s, an average solid-state drive offers up to 550MB/s.
Therefore, when choosing an expansion card for additional SATA ports, you need to make sure you choose one that can offer excellent downstream so that your SSD doesn’t suffer any bottleneck.
For instance, if an x4 connector uses two PCIe lanes and comes with a version 3.0 standard, it’ll be able to provide a speed of about 1700MB/s. With this speed, we can deduce that operating four different hard drives with a speed of 200MB/s at the same time will cause no bottleneck. But operating four different SSDs with a speed of 550MB/s will cause your drives to have performance bottlenecks.
-
You May Not Need to Worry About Bottlenecks
Depending on your setup, it’s likely that not all the drives connected to the SATA expansion card will work at the same time. Therefore, you may not need to worry about performance bottlenecks.
Drives will remain idle until you access files from them, carry out an installation, or when you read or copy from them. However, it’s important that we mention the possibility of a performance bottleneck.
– RAID or Non-RAID SATA Expansion Card
 The last important factor to consider when choosing a SATA expansion card for additional SATA ports is whether you want one with a built-in hardware RAID controller or not. SATA expansion cards with RAID controllers tend to be expensive than those without them. They also use more bandwidth and are often utilized by professionals and NAS builders.
The last important factor to consider when choosing a SATA expansion card for additional SATA ports is whether you want one with a built-in hardware RAID controller or not. SATA expansion cards with RAID controllers tend to be expensive than those without them. They also use more bandwidth and are often utilized by professionals and NAS builders.
Conclusion
We’ve covered the different types of solutions available on how to add more SATA ports to your computer’s motherboard, so here is a quick summary to keep in mind:
- Additional SATA ports allow you to add more drives to your computer
- There are three main types of SATA ports, including SAS SATA expansion cards, SATA hub multiplier, and SATA PCIe card
- SATA PCIe cards are utilized for typical builds
- SATA hub multipliers are often used for budget builds
- SAS SATA expansion cards are used by professionals
- SATA hub multipliers are not recommended as they tend to cause performance bottlenecks
- Make sure you consider the slot version, number of ports, size, and PCIe lanes utilized by your expansion card before making a purchase
- Unless you’re a professional, you may not need an expansion card with a RAID controller
- SATA expansion cards with RAID controllers tend to be pricier than cards without them
And that covers everything on how to add more SATA ports to your computer. With the types and factors we’ve shared above, we believe you have a better understanding of how expansion cards work and how to choose the ideal one for your build.
Keep in mind that what you’ll get with a typical PCIe expansion card isn’t the same as what you’ll get with a professional NAS card with RAID configuration.